Definition of north finding
The definition of north finding is to find true north, not magnetic north, and the north seeking methods mentioned in this article are all described closely around true north.
True north refers to the Earth’s north pole, which is the intersection of 90° north latitude or the meridian. It is also known as true north. It is the direction that passes through a point on the Earth and points toward the Earth’s geographical north pole. The tangent direction of the true meridian passing through a certain point on the earth’s surface becomes the true meridian direction of that point.
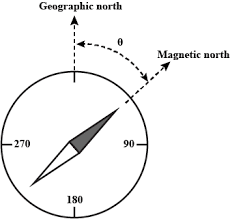
Magnetic north is the north indicated by a compass, primarily because the poles of the Earth’s magnetic field do not coincide with the geographic north and south poles. Therefore, the north indicated by a compass is magnetic north, not true north, and magnetic north changes over time.
North finding uses a gyroscope to measure the component of the earth’s rotation angular velocity combined with the acceleration value, and then calculates the angle with true north to obtain the azimuth angle value.
The methods of north finding
North seeking mainly includes two north seeking methods: static north seeking and dynamic north seeking. The application principles of these two north seeking methods are introduced below.
Principle of static north finding
Static north seeker includes MEMS gyro north seeker and fiber optic gyro north finder.
Principle: The rotation axis of the gyroscope maintains a constant direction relative to the inertial space, while the Earth rotates around the polar axis relative to the inertial space at its rotational angular velocity. If you use the Earth as a reference, you will see that the gyroscope’s axis of rotation rotates relative to the Earth, so the gyroscope can track and measure the angular velocity of the Earth’s rotation.
MEMS gyro north seeker, which has an input axis and a rotation axis. The sensor includes a motor drive structure, a motor signal output from the motor drive structure, a gyroscope, and a sensor rate for the sensor rate signal output from the gyroscope.
Fiber optic gyro north seekers are mainly used to quickly and autonomously determine the true north direction. The Earth’s rotation angular velocity is obtained through high-precision fiber optic gyroscope tracking, and the Earth’s rotation angular velocity signal is decomposed and solved to calculate the angle between the gyroscope’s main axis and the Earth’s true north to provide the carrier with orientation information.
Principles of dynamic north finding
Dynamic north seeking includes fiber optic gyro compass and fiber optic gyro compass (vehicle, ship, airborne)
Principle: Use the strapdown compass effect to find the direction of true north.
The fiber optic gyro compass consists of: three-axis dynamically adjustable gyroscope, three-axis acceleration sensor, data acquisition and processing module, secondary power supply, optocoupler isolated input and output serial port circuit and other related structural parts.
With so many methods available, they are suitable for different circumstances and are not one-size-fits-all. For north seekers used in most fields, inertial measurement device FOG north seekers and MEMS north seekers are relatively advanced in technology.
Comparison of various gyro north seeking systems
By comparing two gyro north-seeking systems, we discovered the similarities and differences between the static north-seeking method and the dynamic north-seeking method.
Common points:
1.They all use the precession and axis fixation of the gyroscope to be sensitive to the earth’s rotation angular speed.
2.The working principle uses the characteristics of the edge of the gyro chamber, that is, the effect of gravity.
Differences:
1.Theoretical differences
The gyroscopic north seeker uses the output of the gyroscope and accelerometer to calculate its azimuth relative to true north to achieve north seeking. Compared with gyro azimuth and gyro compass, it has the advantage of fast north finding speed. However, during the process of north seeking, due to the short start time of the gyro when the gyro north seeker seeks north, there is a gyro drift trend term that is difficult to eliminate, and this term gradually decreases as the gyro starts. The time increases, so the length of time the gyroscope is activated when the north-seeking instrument seeks north has a great influence on its north-seeking accuracy.
2.Differences in application scenarios
Gyrocompasses are mainly used for navigation, such as ships, submarines, UAVs, weapon systems and reconnaissance platforms, providing high-precision azimuth, attitude, navigation and control information. The ER-FGC-2C high-precision gyrocompass has the characteristics of small size, good stability, and high precision, and is fully suitable for navigation in ships, submarines, drones, etc.
Gyro theodolite is mainly used for measurement of large-scale projects such as mines and tunnels. The gyroscope part provides accurate azimuth reference. At the same time, gyro-theodolite can also be used for weapon system aiming.
Gyro-theodolite has high north-finding accuracy, but it cannot be used on mobile carriers such as airplanes and ships because the suspended gyroscope is suspended from the instrument box with a flexible metal belt. On a moving carrier, the instrument shell moves with the carrier. Severe vibrations will cause the flexible metal belt to loosen and fail to maintain a tight state, causing the gyroscope’s movement to lose its original pattern and become unable to work.
3.Differences in performance features (north seeking time and north seeking accuracy)
The north seeking time of the gyro north seeker is short, generally within 5 minutes, and the accuracy can reach about 0.1’. At the same time, there are very few north seekers that can achieve this level of accuracy. ERICCO’s ER-FNS-02 high-precision FOG north seeker has an accuracy of (0.02°-0.1°) and is used for high-precision initial alignment and direction control solutions, which provides a lot of convenience for work. Accuracy can improve relatively over time. The north-finding time of a gyro-theodolite generally takes about 5 to 20 minutes, and the accuracy can reach 10”.
Most recommended north finding equipment
Through the analysis of the two types of north seeking methods, the most suitable north seeking tools for us to use in most fields are MEMS north seekers, FOG north seekers, etc.
The fiber optic gyroscope north seeker uses a closed-loop fiber optic gyroscope as the core component. It is mainly composed of an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a digital signal processing unit and a mechanical part. Provides true north azimuth for the carrier.
The ER-MNS-06 MEMS north seeker is the world’s smallest three-axis MEMS north seeker. It consists of a three-axis MEMS gyroscope and an accelerometer and can measure true north. It has the characteristics of small size, light weight, low power consumption and resistance to harsh mechanical environments, and is widely used in mining, tunnel construction and other fields.
When choosing the most appropriate north-finding device, both gyro-theodolite and gyro-north-finder achieve north-finding on a static basis. Therefore, we can start from the respective characteristics of these two types of devices and complement each other in research or use to achieve coordination of north-seeking accuracy and north-seeking speed.
This article introduces the brief knowledge of the north-finding method. I hope you have a basic and clear understanding of the north-seeking method. If you want to know more about north seeking, you can find useful content in “More Technical Questions”. If you are interested in north finder related products, you can click on “Products in article”. For any questions, please leave your opinions in ‘Ask a Question’ below.
If you need a north seeker, you can send your needs directly to the email . We will send the price and catalog to you!
E-mail:info@ericcointernational.com






.jpg)
