The tilt sensor is a very accurate measuring tool for small angles. It can measure the inclination of the measured plane relative to the horizontal position, the parallelism and perpendicularity of the two components. It has become an indispensable and important measuring tool in bridge construction, railway laying, civil engineering, oil drilling, aviation and navigation, industrial automation, intelligent platform, mechanical processing and other fields.
1. The principle of tilt sensor
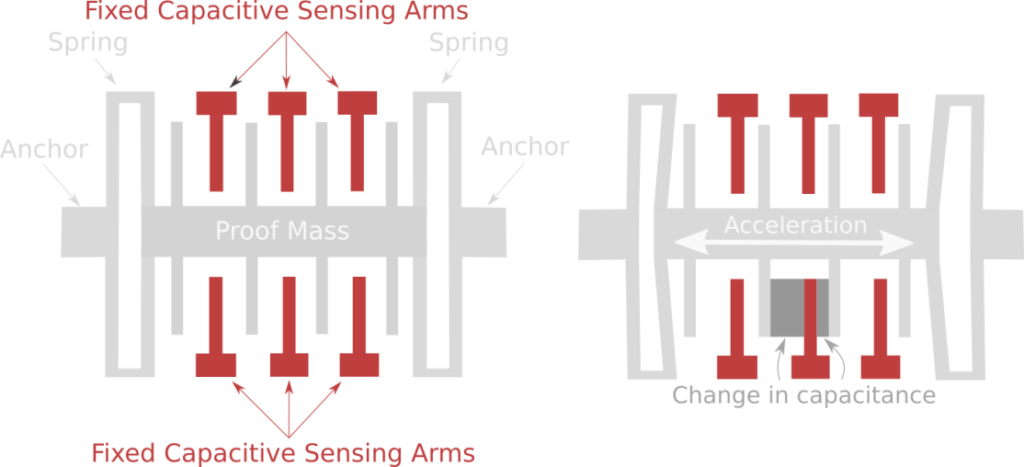
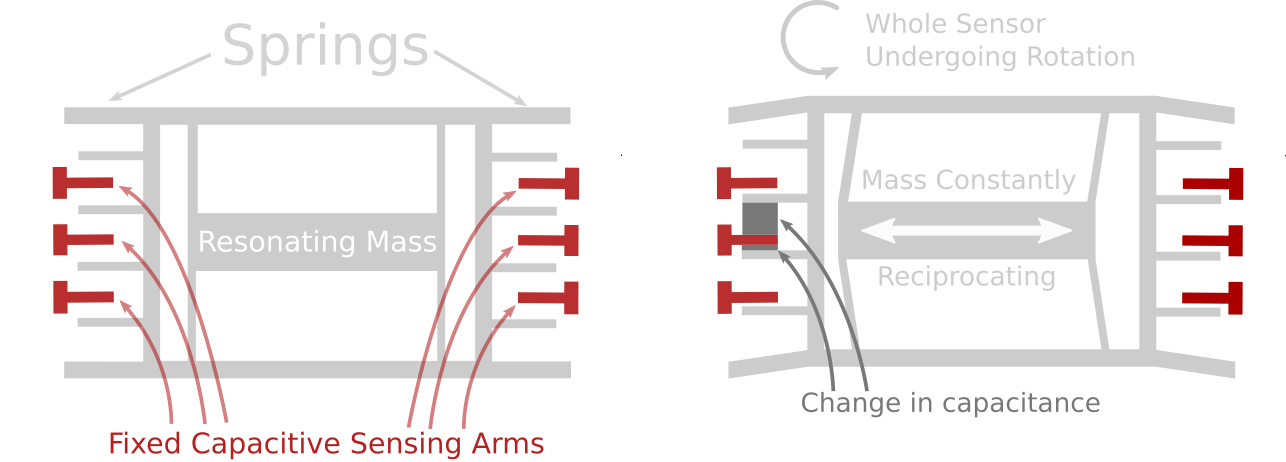
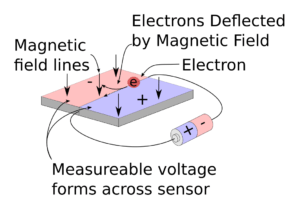
The working principle of the inclination sensor is based on microelectromechanical system (MEMS) technology and accelerometer principle. It is equipped with tiny accelerometers, and by using gravity, inertia and other mechanical principles, to detect the object’s tilt angle relative to the Earth’s horizontal plane.
When the object is at rest, the tilt sensor is subjected to gravity, which causes the accelerometer to align with the vertical direction of the Earth. When the object tilts, the direction of the accelerometer changes accordingly, resulting in an electrical output indicating the angle and direction of the object’s tilt.
2. Advantages of tilt sensor
The main benefits of tilt sensors include:
2.1 High Precision
The tilt sensor adopts MEMS technology, which has the characteristics of high precision, high stability and low noise, and can realize the high precision measurement and control of the tilt angle of the object. ER-TS-12200-Modbus is a high-precision wireless inclination sensor, its accuracy can reach 0.001°, using industrial MCU, three-proof PCB board, imported cables, wide temperature metal shell and other measures, its industrial design has extremely high measurement accuracy and anti-interference ability. It is suitable for remote real-time monitoring and analysis of industrial sites, dilapidated buildings, ancient buildings, civil engineering, tilt deformation of various towers and other needs.
2.2 Compact and Lightweight
The tilt sensor is small in size, light in weight, easy to install and carry, and is suitable for various occasions and environments. ER-TS-32600-Modbus its volume is 94*74*64mm, weight is only 460g, very easy to install and carry. Is an ultra-low power consumption, small volume, high-performance wireless inclination sensor, it uses lithium battery power, based on the Internet of Things technology Bluetooth and ZigBee(optional) wireless transmission technology, it meets the needs of users in industrial applications without power supply or real-time dynamic measurement of object attitude angle.
2.3 High Reliability
The tilt sensor has high vibration resistance, impact resistance, water and dust resistance, and can run stably in complex environment for a long time. For example, the ER-TS-3160VO, which has a seismic resistance higher than 20000g, is adopted IP67 protection grade, it has the characteristics of strong shock and vibration resistance, especially suitable for a variety of harsh industrial environments.
Summary: With the continuous development of technology, inclination sensors will have wider prospects and advantages.
1. High precision and stability: With the continuous improvement of measurement accuracy and stability requirements in various fields, the future development direction of inclination sensors will be to improve the accuracy and stability of induction components.
2. Multi-functional: the inclination sensor will gradually develop in the direction of multi-functional, such as integrating the functions of gyroscopes, magnetometers and other sensors to achieve the measurement of a variety of parameters.
3. Intelligent: inclination sensor will be combined with artificial intelligence, internet of things and other technologies to achieve intelligent perception and data processing, improve application efficiency and user experience.
4. Miniaturization: In order to meet the application needs of some special scenarios, the volume of the inclination sensor will gradually shrink and develop in the direction of miniaturization.
5. Wide application: With the continuous progress of inclination sensor technology and the expansion of application scenarios, its application in various fields will be more extensive, bringing more convenience to people’s life and work.







.jpg)
