The gyro-theodolite is an instrument that combines a gyroscope and a theodolite. Because it is not limited by time and environment, and its observation is simple, convenient and efficient, it can ensure high orientation accuracy (the error of one orientation is between 5" and 2' ), that is, except for high latitude (usually above 75°) areas on the earth, the true meridian position of any point on the ground or underground and the geodetic azimuth angle of any survey line can be measured, and the orientation accuracy is not affected by altitude. In addition to being used for detection In addition to core and alternative geometric orientation, the direction-attached conductor can also be formed by appropriately adding gyro directional edges on long branch conductors to improve conductor point accuracy.
Characteristics and principles of gyro-theodolite
1.Characteristics of gyroscopic theodolite
The gyro-theodolite is a high-precision measuring instrument that is widely used in geodetic surveying, engineering surveying, aerial photogrammetry and other fields. Its characteristics are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1.1 High precision: The gyro-theodolite has extremely high precision and can accurately measure angles and directions, providing reliable data support for all types of measurement work.
1.2 Good stability: The instrument has a stable structure, is less susceptible to external interference, and can maintain high measurement accuracy in complex environments.
1.3 Easy to operate: The gyro-theodolite is reasonably designed and easy to operate. Even people without professional training can get started quickly.
1.4 High degree of automation: Modern gyro-theodolite often integrates automatic control systems, which can realize automatic leveling, automatic recording and other functions, greatly improving work efficiency.
1.5 Wide scope of application: Gyro-theodolite is not only suitable for land measurements, but also for maritime and aerial measurements, and has strong adaptability.
2.Principle of gyro-theodolite
The working principle of the gyro theodolite is based on the fixed axis and precession of the gyroscope. A gyroscope is a device that uses the rotation characteristics of a gyroscope to measure angular velocity. It mainly consists of a gyroscope rotor, a bracket and a measurement system.
2.1 Fixed axis: The fixed axis of the gyroscope means that when there is no external moment, the rotation axis of the gyro rotor will remain unchanged in the inertial space or rotate at a constant speed around a fixed point. This is the basis for the stable operation of the gyro-theodolite.
2.2 Precession: When the rotor axis of the gyroscope is acted upon by an external moment, the rotor axis will precess around a fixed axis perpendicular to the axis of the external moment, which generates a precession angular velocity. By measuring this precession angular velocity, the magnitude and direction of the external torque can be indirectly derived.
In a gyro theodolite, the gyroscope is used to measure the component of the earth's rotation angular velocity on the vertical axis of the instrument, thereby determining the angle between the vertical axis of the instrument and the geographical North Pole axis, that is, the latitude angle. At the same time, by observing the precession of the gyroscope's rotation axis in the horizontal plane, the angle between the geographical meridian direction and the vertical axis of the instrument, that is, the longitude angle, can be measured.
3.Precision orientation method of gyro-theodolite
The precision orientation methods of gyro-theodolite mainly include the reversal point method and the mid-heaven method.
The reversal point method uses a gyro-theodolite to track and observe the horizontal dial readings when the swinging index line (gyro axis) repeatedly reaches the east and west reversal points, and determines the true north direction of the station through calculation. This method requires keeping the instrument stable during the observation process to ensure accurate readings.
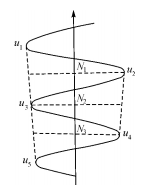
Figure 1 Observation using the reversal point method
The Zhongtian Rule is to first determine the approximate north direction by observing the operation of the gyroscope axis, and then continuously read and record the time when the swinging indicator line (gyro axis) repeatedly passes through the zero line of the reticle plate, and reaches the east and west reversal points. The horizontal dial reading at the time. Through calculation, the correction number of the approximate north direction can be obtained, and then the true north direction of the station can be determined. This method requires precise control of observation times and readings to obtain accurate orientation results.
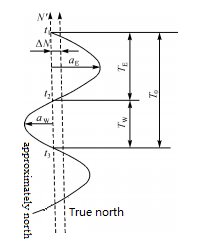
Figure 2 Observation using the reversal point method
Summarize
To sum up, the gyro theodolite achieves high-precision measurement of geographical coordinates by utilizing the gyro's fixed axis and precession properties. In theoretical research and practice, the following consensus has been gradually reached on the number of additional gyroscopic edges: adding gyroscopic edges in long underground wires can effectively control and reduce lateral errors and improve accuracy. Compared with the azimuth angle without additional measurement of the gyro side, the accuracy gain is larger. When one additional side is measured, the gain is 50% to 60%; when three additional sides are measured, the gain is 75% to 80%. If there are more than 3 gyro edges, the gain is not obvious. From the perspective of improving accuracy and measuring personnel's workload, it is appropriate to measure 1 to 2 more gyro edges.
As the accuracy of gyroscopes gradually improves, the advantages of gyroscope orientation will become more obvious, and their application in underground engineering conductors such as mines and tunnels will become more common. ERICCO's gyro theodolite, such as ER-GT-02 and ER-GT-03:
ER-GT-02 (≤3.6") Features:
- Orienteering accuracy ≤3.6" (1σ);
- Pit interference ability is strong, integrated fuselage design, compact structure, stable performance;
- Has the functions of low lock, automatic zero observation and etc.
ER-GT-03 (≤30")Features:
- Orienteering accuracy ≤30" (1σ);
- Volume (no theodolite) ≤Φ200mm×h490mm.
Welcome to learn more, please contact us.


.jpg)

No comments:
Post a Comment